Laboratory of Virology and Infectious Disease
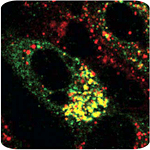
HCV core protein (green) accumulates on the surface of lipid droplets (red).
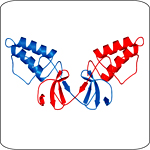
Crystal structure of the HCV NS2 protease domain shows a dimer with an unusual composite active site.
Virus Assembly and Release
In 2005, almost twenty years after the discovery of HCV as the major causative agent of non-A non-B hepatitis, the entire infectious cycle of the virus was recapitulated in cell culture for the first time. Our laboratory and others succeeded in developing the cell culture system by exploiting a unique genotype 2a patient isolate, Japanese fulminant hepatitis-1 (JFH-1), which both replicates to high levels and supports the release of infectious particles. The advent of the cell culture system has at last allowed authentic virus entry, assembly, and egress to be investigated in the laboratory.
Structural proteins make up the physical virion, and include core, E1, and E2. We have shown that the HCV core protein is essential for infectious virus production and are continuing to map the determinants important for this activity. Nonstructural proteins are not part of the virus particle but can be required for its formation. We have found that both p7 and NS2 play essential roles in producing infectious HCV, possibly through their interactions with the structural proteins. NS2 is a multifunctional protein that also possesses protease activity. We have determined the X-ray crystal structure of the NS2 protease domain and found it to be an unusual dimeric enzyme with two composite active sites. This protease domain is essential for the role of NS2 in infectious virus assembly, although the catalytic activity of the enzyme is not. Understanding how infectious virus particles are formed may lead to new classes of inhibitors targeting assembly.
Further reading
- Lindenbach BD, Evans MJ, Syder AJ, Wölk B, Tellinghuisen TL, Liu CC, Maruyama T, Hynes RO, Burton DR, McKeating JA, Rice CM. Complete replication of hepatitis C virus in cell culture. Science. 2005 Jul 22;309(5734):623-6.
- Jones CT, Murray CL, Eastman DK, Tassello J, Rice CM. Hepatitis C virus p7 and NS2 proteins are essential for production of infectious virus. J Virol. 2007 Aug;81(16):8374-83.
- Kopp M, Murray CL, Jones CT, Rice CM. Genetic analysis of the carboxy-terminal region of the hepatitis C virus core protein. J Virol. 2010 Feb;84(4):1666-73.
- Lorenz IC, Marcotrigiano J, Dentzer TG, Rice CM. Structure of the catalytic domain of the hepatitis C virus NS2-3 protease. Nature. 2006 Aug 17;442(7104):831-5.