KvAP Crystal Structure
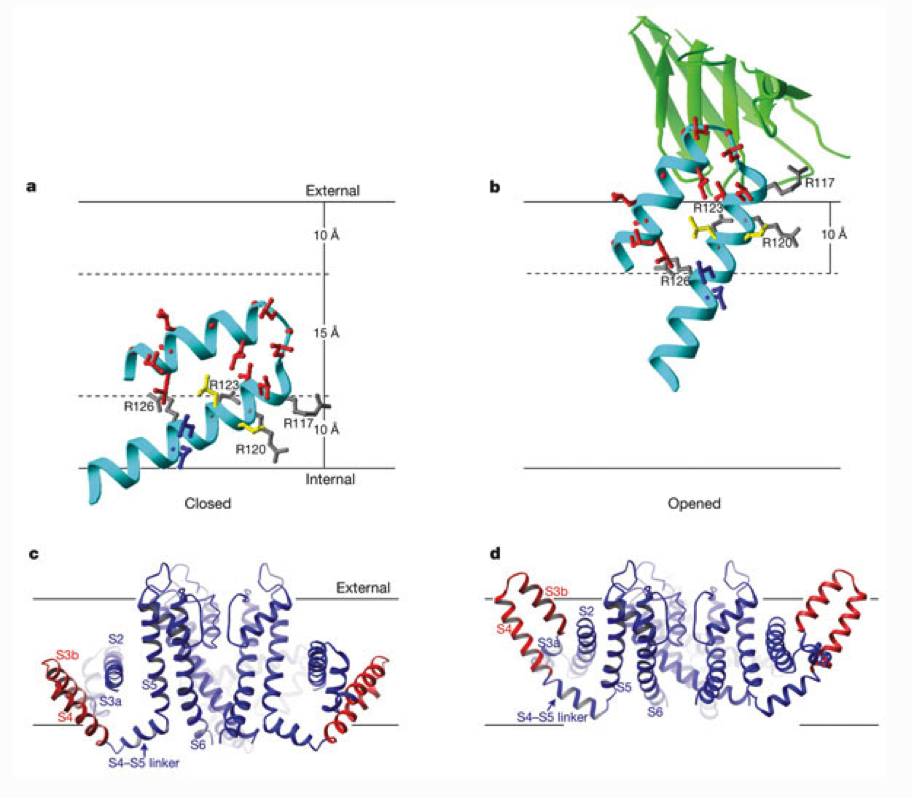
a, b, Closed (a) and opened (b) positions of the paddles derived from the tethered biotin–avidin measurements, and structural and functional measurements with Fabs. A voltage-sensor paddle is shown as a cyan ribbon with side chains colour-coded as in Fig. 3. Grey side chains show four arginine residues on the paddle, and the green ribbon (b) shows part of a bound Fab from the crystal structures. Solid horizontal lines show the external and internal membrane surfaces, and dashed lines indicate the 10-Å distance from the surfaces set by biotin and its linker. c, The closed KvAP structure is based on the paddle depth and orientation in a (red), and adjusting the S5 and S6 helices of KvAP to the positions in KcsA, a closed K+ channel. d, The opened KvAP structure is based on the paddle depth and orientation in b (red), and the pore of KvAP.
Jiang, Y., Ruta, V., Chen, J., Lee, A., MacKinnon, R. (2003). The principle of gating charge movement in a voltage-dependent K+ channel. Nature, 423, 42-48. doi: 10.1038/nature01581